Using ADO Control
Now you will learn how to create ADO-based applications.
We will use the sample BIBLIO.MDB database that comes
with Visual Basic. The source code needed for this
example is stored in the "Source Code\Chapter23\ADO
Control " directory.
First, you must connect the control to the data the
control will access. You can connect a data source
to the ADO control in two ways:
- Set the ConnectionString property.
- Use code to connect the control to the data.
Create a new application. Press Ctrl+T to open the
Components dialog box and select Microsoft Active
Data Control 6.0 to place the ADO control on the tollbox.
Add the control to the form. Now click the ConnectionString
property, the dialog box shown in the following appears:
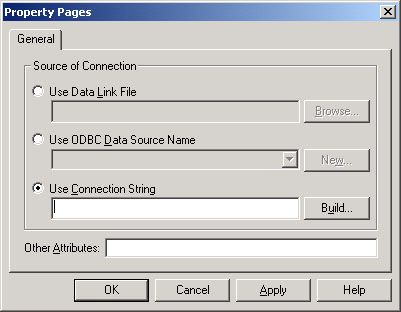
For this simple example, the first two options, a
Data Link File option and an ODBC file option, are
not needed. Click the third option to specify a connection
string. Follow the following steps to build the connection
string:
- Click the build button to display the Data Link
Properties dialog box.
- Double click the first option labeled Microsoft
Jet 3.51 OLE DB provider.
- Click the ellipses button to the right of the
first text box and locate BIBLIO.MDB database.
- Click the OK button to return to the first Property
Pages dialog box page; then click OK to close the
dialog box and return to your form.
Now Double click the RecordSource property and select
the following:
- Command Type: 2-adCmdtable
- Table Name: Authors
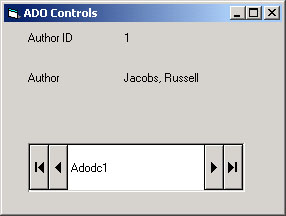
Now add label controls to the form and bind them.
You learned to do this kind of binding with the simple
Data control. When you run the application, you will
see the following:
 |
|
| Today's lesson
explained database access with Visual Basic.
The simplest way to access a database is to
add the data control to your form. Methods can
be used to extend the functionality of the data
control. The ADO interface requires extensive
programming, but you get much more control and
flexibility when accessing your database. |
|